Automating EC2 and Tailscale with Terraform
Overview
This project demonstrates the integration of AWS EC2 and Tailscale using Terraform and Bash scripting. It automates the deployment of VPCs, subnets, EC2 instances, and the setup of Tailscale for secure networking. The code also configures EC2 instances to display instance metadata and acts as Tailscale subnet routers.
Key Features
AWS EC2 Instance Metadata Display
A Bash script is used to retrieve EC2 instance metadata such as instance ID, AMI ID, instance type, and availability zone. This data is displayed through an Apache web server hosted on the instance.- Tailscale Integration
- Authentication Key Creation: Terraform generates a reusable, preauthorized, and ephemeral Tailscale authentication key for secure connections.
- Subnet Router Configuration: Instances advertise private subnet routes via Tailscale, enabling secure communication between private networks.
- Network Forwarding: Configures IPv4 and IPv6 forwarding to support Tailscale subnet routing.
- Dynamic Multi-City AWS Infrastructure
- Deploys a unique VPC, subnet, internet gateway, and route table for multiple cities using Terraform.
- Each city corresponds to its own EC2 instance with distinct IP ranges.
- Security Groups
- Configures ingress and egress rules to allow SSH and HTTP access while maintaining security.
- Instance Configuration with Startup Scripts
- Automatically installs and configures Apache, retrieves instance metadata, and sets up Tailscale during instance initialization.
Example Terraform Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
variable "city_names" {
default = ["Calgary", "Toronto", "Vancouver"]
}
resource "aws_vpc" "vpc" {
count = var.city_names.length
cidr_block = "10.${count.index + 1}.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags = {
Name = var.city_names[count.index]
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "instance" {
count = var.city_names.length
ami = "ami-0ba992fa05aaa4a76"
instance_type = "t3.nano"
subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet[count.index].id
key_name = aws_key_pair.keypair.key_name
user_data = templatefile("startup_script.sh", {
tailscale_auth_key = tailscale_tailnet_key.multi-site-authkey.key
private_subnet_cidr = aws_subnet.subnet[count.index].cidr_block
tailscale_name = "${var.city_names[count.index]}-instance"
})
tags = {
Name = "${var.city_names[count.index]}-instance"
}
}
Results
- Multi-City Deployment: Instances and networks are dynamically created for each city with unique CIDR ranges.
- Tailscale Subnet Routing: Secure connections are established between private networks in different cities.
- Automation: Metadata retrieval, Apache configuration, and Tailscale setup are fully automated, reducing manual effort.
Tailscale Admin Console: 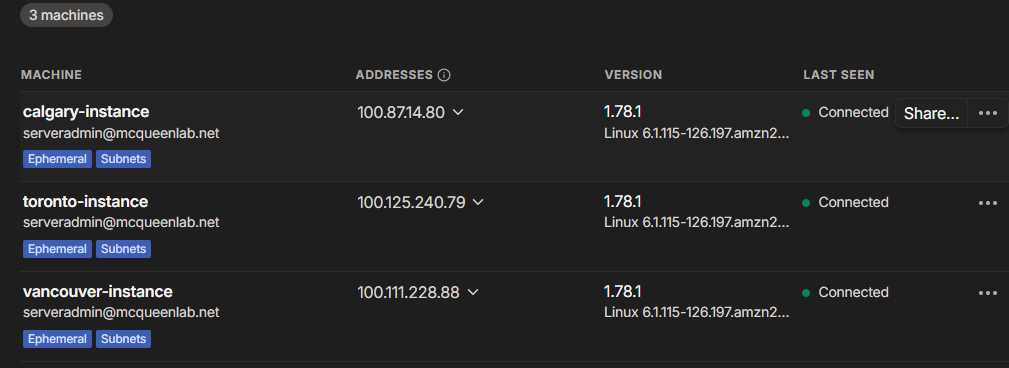 As you can see it has already accepted the routes that the subnet router is creating. No manual configuration needed at any step!
As you can see it has already accepted the routes that the subnet router is creating. No manual configuration needed at any step!
Final Thoughts
This project highlights the power of combining Terraform, Bash scripting, and Tailscale for scalable, secure, and automated infrastructure management. By automating repetitive tasks and leveraging Tailscale’s capabilities, managing complex cloud networks becomes more efficient and secure.
The full repository with all scripts and Terraform code can be found here.

